![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some aspects of the head and neck physical exam that I might be easy to forget? (3)
|
1) palpate temporal arteries
2) palpate TMJ 3) inspect and palpate lymph nodes of head |
|
|
What are the lymph nodes of the head?
|
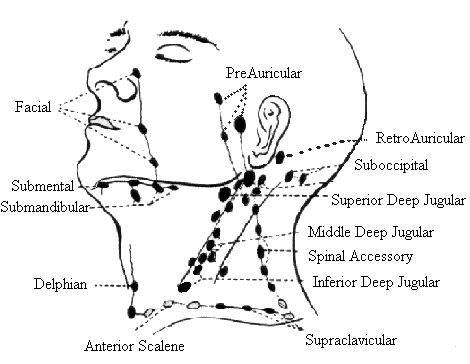
</img>
1) preauricular - in front of ear 2) posterior auricular - superficial to mastoid process 3) occipital - base of skull posteriorly 4) tonsilar - at angle of mandible 5) submandibular - midway between the angle and the tip of mandible 6) submental - in the midline a few centimeters behind the tip of the mandible 7) superficial cervical - superficial to sternomastoid 8) posterior cervical - along the anterior edge of the trapezius 9) deep cervical chain - deep to sternomastoid and often inaccessible to examination 10) supraclavicular - deep in the angle formed by the clavicle and sternomastoid |
|
|
What is the difference between Weber and Rinne?
|
Weber is fro laternalization and Rinne is for air conduction vs bone conduction
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the pneumatic otoscope?
|
mobility of eardrum
|
|
|
What are some of the biological changes of aging?
|
1) presbycusis
2) chewing surface of teeth worn down 3) laryngeal muscles lead to higher/tremulous voice |
|
|
What are aspects of the head and neck that are unique to children?
|
1) fontanelles
2) neck lymph nodes 3) pnuematic otoscope for otitis media 4) palate examined in new borns 5) dental exam |
|
|
When do the fontanells close?
|
anterior: 2 months
posterior fontanelle 2 years |
|
|
What is different about the lymph nodes in children
|
enlarged but mobile.
fixed lymph nodes mean ther could b ea problem |
|
|
When do teeth emerge?
|
6-9 months
|
|
|
When are all primary teeth present?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When do adult teeth appear?
|
age 6
|
|
|
How do you write up the Head and Neck Exam:
|
HEENT:
Head: Ears: Sinuses Nose: Mouth: Neck: |
|
|
What are some things that can be done for patients comfort in the abdominal exam?
|
-remind patient to empty bladder
-warm sethescope/hands of physician -position -draping |
|
|
Is a pot belly normal in older adults?
|
yes
|
|
|
When should the newborns umbilical cord fall out?
|
2 weeks
|
|
|
When are umbilical hernias normal?
|
up to age 4 or 5 in children
|
|
|
What is the liver size in ch ildren?
|
1-2cm below right costal margin
|
|
|
What should be included in a case presentation?
|
1) chief complaint/reason for office visit
2) HPI 3) information from PMH, FH or SH if relevant to HPI 4) observations from physical examination 5) brief comment on significance of case to student |
|
|
preauricular lymph nodes
|
in front of ear
|
|
|
posterior auricular -
|
superficial to mastoid process
|
|
|
3) occipital
|
- base of skull posteriorly
|
|
|
tonsilar
|
at edge of mandible
|
|
|
5) submandibular
|
- midway between the angle and the tip of mandible
|
|
|
6) submental
|
- in the midline a few centimeters behind the tip of the mandible
|
|
|
7) superficial cervical -
|
superficial to sternomastoid
|
|
|
8) posterior cervical -
|
along the anterior edge of the trapezius
|
|
|
9) deep cervical chain
|
- deep to sternomastoid and often inaccessible to examination
|
|
|
10) supraclavicular
|
- deep in the angle formed by the clavicle and sternomastoid
|
|
|
What lymph nodes drain mouth and throat and face? (3)
|
1) tonsillar
2) submandibular 3) submental |

